 Fig. 1: The Sioux People.
Fig. 1: The Sioux People.
date | Event | Significance |
1866-68 | Red Cloud's War | Oglala Sioux established dominance over the U.S. Army |
1868 | Treaty of Fort Laramie | Created the Great Sioux Reservation |
1874 | Gold discovery in the Black Hills | White settlers after the gold rush began encroaching on native land backed by the government. |
May 1875 | Sioux delegates travel to Washington | Spotted Tail, Red Cloud, and Lone Horn traveled to Washington DC to plead with President Grant to honor their treaties and stop the encroachment of white settlers. |
| May 1876 | The Lakota are ordered to return to the reservation | This would set the stage for multiple battles between the Lakota and U.S. armed forces. |
| June 1876 | Battle of the Rosebud | Crazy Horse and the Sioux fought General Crook's troops. |
| June 1876 | Battle of Little Bighorn | Crazy Horse and Sitting Bull led a fight against Custer and the 7th Cavalry. |
| May 1877 | Crazy Horse Surrendered | Many bands of natives began to surrender, leading to the end of the war. |
The Great Sioux War of 1876
The Great Sioux war was a series of battles between 1876 and 1877 that pitted the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States.
 Fig. 2: The Black Hills.
Fig. 2: The Black Hills.
Reasons for the Great Sioux War
Gold was found in the Black Hills of South Dakota in 1874. In the spring of 1874, General Philip Sheridan directed a lower-ranking officer, Brigadier General Alfred Terry, to travel to the Black Hills to see if the land would be suitable for an army garrison. Not only did they find that the land would work well for a garrison, but they discovered gold in the Black Hills.
Garrison:
A group of soldiers that live in and are responsible for the defense of a town or fort
After the gold strike, the United States federal government was hungry to obtain access to the Black Hills. White settlers began to encroach on the land that belonged to Native Americans after the gold rush, which was a clear violation of the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie. The Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne refused to cede their land to the government.
Cede:
To give up rights to an area of land.
Reservation:
An area of land set aside for Native Americans to live on.
President Ulysses S. Grant found himself between a rock and hard place. He had a moral conundrum: could he deny the American people the pursuit of happiness even if they wanted to hunt for gold? Could he legally allow them on the land?
 Fig. 3: Ulysses S. Grant.
Fig. 3: Ulysses S. Grant.
In 1875, Sioux delegates traveled to Washington to meet with President Grant. Delegates Spotted Tail, Red Cloud, and Lone Horn begged him to honor their existing treaties and stop the encroachment of white settlers on their land. Instead, the president offered them money and the opportunity to relocate to the Indian Territory in modern-day Oklahoma. The delegates refused the offer.
The next stage was war. President Grant did not directly attack the Sioux living on the reservation. Instead, he decided to go after those on unceded land, which did not technically belong to the Sioux. The government did not recognize their ownership of the land, but it did not deny that they had the right to hunt there.
President Grant commanded the Bureau of Indian Affairs to order all Native Americans on the unceded land to return to the reservation on their own to report to one of the agencies on the reservation or be forced back by the military. Most of the Native Americans on the unceded land did not obey. When their deadline passed, the War Department ordered a military campaign against them. Those who hoped to remain off-reservation aligned themselves with Sitting Bull. This was the beginning of the Great Sioux War.
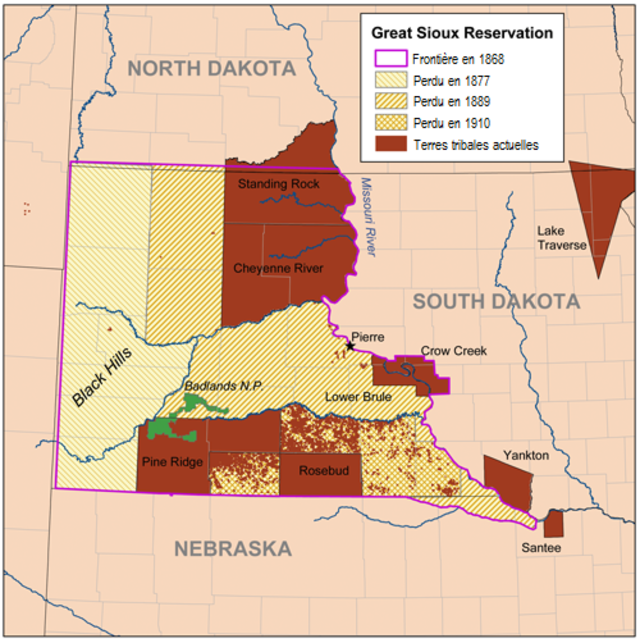
Fig. 4: Sioux Reservation Map.
- In May 1876, the United States Army began to force the Lakota back onto their reservation.
- There were three parts to their attack: Colonel John Gibbon traveled towards the Great Sioux Reservation from Fort Ellis in Montana.
- General George Crook traveled towards the Great Sioux Reservation from Fort Laramie.
- General Alfred Terry and George Custer traveled toward the Great Sioux Reservation from Fort Abraham Lincoln in North Dakota.
The Army's campaign began to fall apart when Crazy Horse led the Sioux to turn back General Crook's troops in the Battle of the Rosebud.
Shortly after this, Custer's cavalry attacked a Native American camp on the Little Bighorn River. Custer attempted to divide his troops and attack the camp from two directions, however, the mission failed. Over 250 troops were killed, including Custer himself. Later, the United States Army would annex the Black Hills from the Great Sioux Reservation.
Did you know?
Custer's Seventh Cavalry later went on to massacre over 250 people at Wounded Knee. It is thought that they committed the shooting to avenge their defeat at the Little Bighorn.
Cavalry:
A branch of the armed forces that fought on horseback.
Annex:
To take control of a territory or area near yours, often by using force.
 Fig. 5: George Custer.
Fig. 5: George Custer.
After this, the Native Americans split into small bands and spread out across the land. The United States Army launched a winter operation and began to hunt down the Sioux who did not report to the federal reservation agencies.
In May 1877, Crazy Horse surrendered at Fort Robinson, Nebraska. He died shortly after while trying to escape. Sitting Bull fled to Canada with nearly 2,000 people joining him.
Consequences of the Great Sioux War
This was different from Red Cloud's War fought in 1866. Very few of the Sioux were supportive of the war. Most of them had settled in the reservations and were utilizing the rations provided by the government.
The end of the Great Sioux War marks the beginning of the Reservation Era. Sitting Bull, who had fled to Canada with thousands of followers, returned to the United States in 1881. At this point, all the Lakota Sioux were living on the Great Sioux Reservation.
This led to a political divide within the Sioux nation, with many later joining the Ghost Dance movement of 1889-1890.
Treaty of Fort Laramie
In the 1860s, there was an extreme amount of violence between the Sioux people and American soldiers. To address the issue and potentially solve the problem, a military commander named William Tecumseh Sherman called the Sioux to council at Fort Laramie. The Sioux were told to stop fighting, move to the reservation, or face the consequences.
The Treaty of Fort Laramie was signed in 1868, establishing a 60-million-acre reservation for the Sioux people.
The Lakota people, part of the Sioux, signed a treaty with the U.S. Federal Government to relocate to the reservation. They had to commit to staying on the reservation and promise that they would not attack any white settlers. In return, the Lakota were promised food rations, education, and other benefits.
 Fig. 6: Sitting Bull.
Fig. 6: Sitting Bull.
The Great Sioux War Summary
The Great Sioux war was a series of battles between 1876 and 1877 that pitted the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States army.
There was a gold rush in the Black Hills of South Dakota in 1874. While this was exciting, it was also problematic. The Black Hills were part of the Great Sioux Reservation, which meant Americans were to stay out of the area.
Unfortunately, this did not happen. White settlers began to encroach on the area, which violated the 1868 Laramie Treaty. Sioux delegates traveled to Washington to meet with President Grant, begging him to honor the existing treaties and stop the encroachment of settlers on their land. President Grant offered them money for the land, but they refused to cede their land to the government.
Since they could not go to war outright over the land on the reservation, they decided to focus their attention on the Sioux living off the reservation. The government issued an ultimatum to all those living off reservation-return to the reservation agency by the deadline, or they would be prosecuted.
Nearly a dozen battles would be fought over the next two years. The early part of 1877 saw many northern bands of Native Americans beginning to surrender. Chief Sitting Bull led a group of Native Americans into Canada before returning to South Dakota and surrendering in 1881. The end of the Sioux War signaled the beginning of the reservation era.
Great Sioux War - Key Takeaways
- The Great Sioux War was a series of battles fought from 1876 to 1877. There were nearly a dozen battles featuring the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne fighting against the United States.
- These tribes fought the United States in response to the presence of white settlers in the Great Plains. Settlers were encroaching on their territory as they attempted to participate in the gold rush happening in the Black Hills.
- The end of the Great Sioux War signified the beginning of the Reservation era.
- The United States annexed the Black Hills and took back their territory in an act of retribution.
References
- Great Sioux Reservation. Photo by Kmussuer. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Siouxreservationmap.png Lisensed by CC-BY-SA-2.5 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5/deed.en













